Harmonize test execution via Plugin
To make sure, the execution of tests in a running testprogram in different sites is synchronized, the testprogram instance would always wait for a go signal from the Master application to proceed the execution of the next test.
Synchronization Master and Tester
The testprogram execution will be driven by the master application. Therefore, the master should be able to identify the Tester type, ether a Parallel Tester or Single Tester.
In case of Parallel Tester:
The test execution will be synchronized via a wire connection between a Parallel Tester and some Single Testers, e.g.
Each Single Tester will be connected to the Parallel Tester with two different GPIOs
one GPIO is used from the Parallel Tester to signalize execution release
second one is used from the Single Tester to signalize a synchronization request or. one test is executed
In case of only one Single Tester, there is no need to synchronize. the test execution may be automatically released each time a request is triggered
Test Execution Scenario
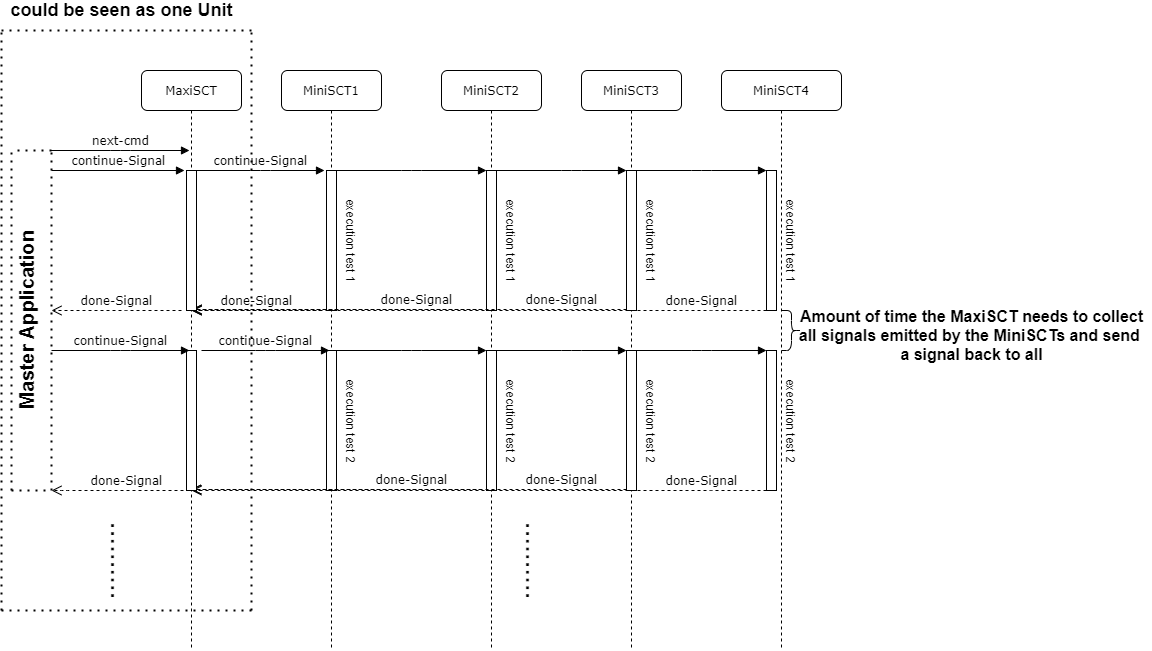
case of Parallel Tester & Single Testers
Before each new test program executes, the Master sends a next command over mqtt to signalize that the Single Tester should change it’s state to testing and be ready to receive the continue-signal to run the first test.
Remark: we still need to keep the next-cmd to transmit user settings infos (e.g. stop-on-fail, etc..)
After each test execution the Single Testers send a Signal to the Parallel Tester to signalize that the test is executed and they are waiting for the continue-Signal to execute the next test
the Diagram below illustrates how the communication Parallel Tester and Single Testers looks like
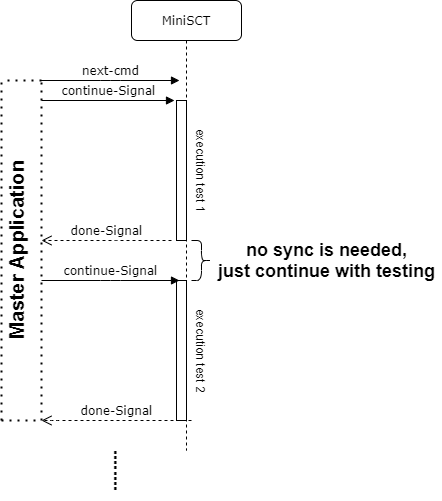
case of only one Single Tester
As we only have one Single Tester, the continue-signal will be simulated by the Single Tester itself. there is not need to synchronize.
Tester Plugin Interface
Master Tester Interface
Master Application shall know how to synchronize the available Single Tester and be able to use the Tester Plugin to control their tests execution.
Tester Plugin should implement the following functions:
def release_test_execution(sites: list)
the release_test_execution function will be used to signalize that the next test for the specified sites, can run. this event is needed as soon as all requests from all defined sites are received.
In case of Parallel Tester, all specified sites will receive a signal to carry on with tests, such that the outputs connected to each of them will be set to high or low according to specification.
In case of Single Tester, there is not going to get a hardware signal since the Single Tester is where we run the tests.
Therefore, the master should in this case send the command via mqtt
or we can simulate the connection and handle all the communication in a file. This approach requires that the master application is running on the Single Tester itself (could be a bit faster than mqtt)
async def get_sites_states(timeout: int) -> list
the get_sites_states is an async function that returns a list of all GPIOs suppose to be connected to a MSCT (list length = 16) within a given timeout.
in case of Parallel Tester, each of the outputs connected to a Single Tester should be read and evaluated
in case of Single Tester, this function could be ignored
TestProgram Tester Interface
Test Program should after each test execution signalize, that it is ready to carry on with the next test, then wait till the master application sends a response to continue the execution.
Tester Plugin should implement the following function:
def do_request(site_id: int, timeout: int) -> bool
do_request function will be called as soon as a next command is received depend on the type of the Tester ether Parallel Tester or Single Tester, we can determine which form the request should take e.g.:
In case of Parallel Tester, set the output connected to the Parallel Tester to high and wait until the release signal is set or timeout
in case of Single Tester: the function will return always true. Tests must not be synchronized in this case.
def test_in_progress(site_id: int)
test_in_progress function signalize the site is busy (e.g testing)
def test_done(site_id: int, timeout: int)
test_done function signalize that the site is done with testing and wait to be released again
def do_init_state(site_id: int)
do_init_state function sets the tester gpio state to low
Signal Flow
The signal flow describes the low-level communication between Maxi- and Mini-SCT. The done-signal is the one controlled by the Mini-SCT, which should switch to high as soon a next-command (over mqtt) is received. the continue-Signal is controlled by the Maxi-SCT.
hint: the states taken by the signals done-Signal and continue-Signal before receiving (case of Single Tester) and sending (case of Parallel Tester) of next command do not affect the system. the next command triggers the state transition of both Maxi- and Mini-SCT to testing and from that point the signal would be significant and should be handled carefully.
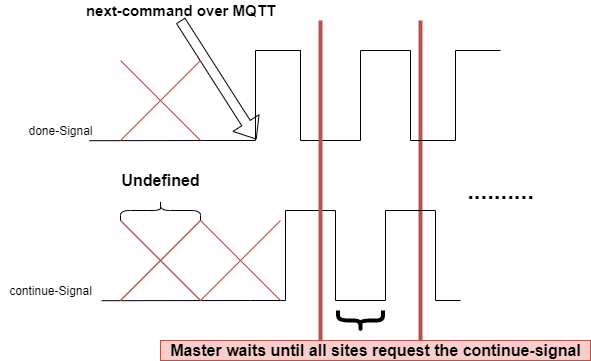
Assuming the next-command is send, and both Maxi- and Mini-SCT update their state to testing. the Single Tester sets the done-signal to high to signalize that its ready to execute. the Parallel Tester shall in that case read the done-signal of all configured sites and sets the continue-signal to high to signalize a test start (all sites should set the done-signal to high)
As soon as the Single Tester executes a test, sets its done-signal to low to signalize the active testing state. the Parallel Tester sets then the continue signal to low and wait until it sees a high done-signal.